Mango, (Mangifera indica L.), belongs to the family of Anacardiaceae, and is frequently found in tropical and sub-tropical regions.
Mango contains a unique xanthonoid called mangiferin. Mango leaves also have significant polyphenol content, including xanthonoids, mangiferin and gallic acid. Mangiferin present in significant levels in different parts of the mango fruit, such as the peel, stalks, leaves, barks, kernel, and stone.
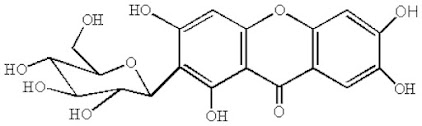
Mangiferin is a significant bioactive constituent of mango containing xanthone-C-glycoside, which has many pharmacological properties and is very important as phytochemical.
Mangiferin (2-β-D-glucopyranosyl-1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxy-9H-xanthen-9-one) possesses several health endorsing properties such as antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, antiallergic, anticancer, hypocholesterolemic, and immunomodulatory. It suppresses the activation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor isoforms by changing the transcription process.
It can promote endothelial cell migration during the angiogenesis and may therefore have promising prevention and therapeutic potentials on vascular diseases. It bears a catechol moiety, which is important for its diverse biological activity.
Previously, mangiferin was extracted by conventional methods such as Sohlex, heat reflux and maceration extraction. With the recent development of novel extraction methods, such as microwave-assisted extraction, ultrasonic extraction, and subcritical fluid, several studies have reported the effectiveness of mangiferin extraction from various sources.
Mangiferin in mango fruit
Nutrition is a scientific discipline that encompasses a structured body of knowledge. It includes various fields such as clinical nutrition, community nutrition, public health, food policy, and food science. At its core, nutrition is the study of how the body utilizes food. It is essential to life. Understanding nutrition enables us to make better dietary choices by determining the necessary nutrient intake, identifying optimal food sources, and recognizing beneficial or harmful food components.
Popular articles
-
Thermization is a controlled, mild heat treatment used in the dairy industry, particularly in cheese production, to reduce microbial levels ...
-
ATP, also called adenosine triphosphate, acts as a way to store energy for future cellular processes or provide immediate energy for the cel...
-
Betalains are a distinctive group of naturally occurring pigments found in a limited number of plants, most notably within the Amaranthaceae...
-
Vitamin B7 or biotin also known as vitamin H. Biotin acts as coenzymes during the metabolism of protein, carbohydrates and fatty acids synth...
-
Dietary fiber has been identified as an important component of a healthy diet. Whole wheat grains are good sources of dietary fiber. It con...