Mango, (Mangifera indica L.), belongs to the family of Anacardiaceae, and is frequently found in tropical and sub-tropical regions.
Mango contains a unique xanthonoid called mangiferin. Mango leaves also have significant polyphenol content, including xanthonoids, mangiferin and gallic acid. Mangiferin present in significant levels in different parts of the mango fruit, such as the peel, stalks, leaves, barks, kernel, and stone.
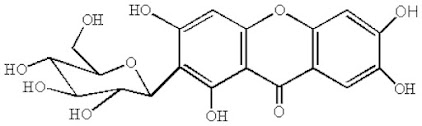
Mangiferin is a significant bioactive constituent of mango containing xanthone-C-glycoside, which has many pharmacological properties and is very important as phytochemical.
Mangiferin (2-β-D-glucopyranosyl-1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxy-9H-xanthen-9-one) possesses several health endorsing properties such as antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, antiallergic, anticancer, hypocholesterolemic, and immunomodulatory. It suppresses the activation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor isoforms by changing the transcription process.
It can promote endothelial cell migration during the angiogenesis and may therefore have promising prevention and therapeutic potentials on vascular diseases. It bears a catechol moiety, which is important for its diverse biological activity.
Previously, mangiferin was extracted by conventional methods such as Sohlex, heat reflux and maceration extraction. With the recent development of novel extraction methods, such as microwave-assisted extraction, ultrasonic extraction, and subcritical fluid, several studies have reported the effectiveness of mangiferin extraction from various sources.
Mangiferin in mango fruit
Nutrition is a scientific discipline that encompasses a structured body of knowledge. It includes various fields such as clinical nutrition, community nutrition, public health, food policy, and food science. At its core, nutrition is the study of how the body utilizes food. It is essential to life. Understanding nutrition enables us to make better dietary choices by determining the necessary nutrient intake, identifying optimal food sources, and recognizing beneficial or harmful food components.
Showing posts with label mangiferin. Show all posts
Showing posts with label mangiferin. Show all posts
Tuesday, May 02, 2023
Thursday, May 16, 2019
Pharmacological properties of mangiferin
Mangiferin
(1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxy-2-[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]xanthen-9-one)
is a naturally occurring polyphenol in several fruits, one being
Mangifera indica L., one of the most popular tropical fruit bearing
trees in the world.
Mango leaves have been used by traditional medicine of a number of peoples for centuries. The key biological substance in them is a polyphenol called mangiferin. Mangiferin commonly used as antioxidant for medical purposes.
Mangiferin inhibited the hydroxyl radicals by 84.3 % at 37 °С and 79.8 % at 80°С, as it showed a higher antioxidant activity than quercetine.
Mangiferin is a heat stable molecule and it possesses antioxidant,
antidiarrhea, dyslipidemic, anti-diabetic, antibacterial and anticancer
activities.
Studies have suggested that Mangiferin also has an in vitro anticancer effect in cellular lines of acute myeloid leukemia. It was also reported Mangiferin as a promising natural product with benefits as analgesic, anti-sclerotic, antiviral, cardio and hepatoprotective, anti-allergic, monoamine oxygenase (MAO) inhibitor, and protector against UV radiation.
These polyphenols of mangiferin exhibit antioxidant properties and tend to decrease the oxygen-free radicals, thereby reducing the DNA damage. Indeed, its capability to modulate several key inflammatory pathways undoubtedly helps installing the progression of carcinogenesis.
Pharmacological properties of mangiferin
Mango leaves have been used by traditional medicine of a number of peoples for centuries. The key biological substance in them is a polyphenol called mangiferin. Mangiferin commonly used as antioxidant for medical purposes.
Mangiferin inhibited the hydroxyl radicals by 84.3 % at 37 °С and 79.8 % at 80°С, as it showed a higher antioxidant activity than quercetine.
Studies have suggested that Mangiferin also has an in vitro anticancer effect in cellular lines of acute myeloid leukemia. It was also reported Mangiferin as a promising natural product with benefits as analgesic, anti-sclerotic, antiviral, cardio and hepatoprotective, anti-allergic, monoamine oxygenase (MAO) inhibitor, and protector against UV radiation.
These polyphenols of mangiferin exhibit antioxidant properties and tend to decrease the oxygen-free radicals, thereby reducing the DNA damage. Indeed, its capability to modulate several key inflammatory pathways undoubtedly helps installing the progression of carcinogenesis.
Pharmacological properties of mangiferin
Thursday, July 31, 2014
Phytochemical mangiferin of mango fruit
A major chemo-preventive phytochemical present in mangoes is mangiferin (1,3,6,7 – tetrahydroxyxanthone – C2-beta-D-glucoside), which is a C-glucosylxanthone. Molecular weight is 422 and its melting point 271 ° C with ferric chloride it gives a positive test.
Mangiferin was found to have cardio-protective activity. Recent studies showed that mangiferin and mango extracts rich in mangiferin increased endothelial cell migration.
In one study dietary administration of mangiferin inhibited benzene (a) pyrene- induce lung carcinogenesis in Swiss albino mice.
The result suggested that mangiferin present in mango extracts may have health promoting effects in diseases related to the impaired formation of new blood vessels.
The formation of new blood vessels is an important therapeutic target for diseases such as limb ischemia, coronary infarction or stroke.
It also reported that mangiferin inhibits tumor growth in early and late stages of cancer.
The easiest source of mangiferin is the mango plant – Mangifera indica, especially the leaves of the plant. Stem bark, heartwood and roots of Mangifera indica also yield mangiferin. It is synthesized in leaves and remains stored at bark. During flushing, mangiferin is mobilized into the growing region and is utilized in forming new shoots and leaves.
Mangiferin being phenolic in nature also acts as a defensive chemical compound of the plant. Besides it serves as the carrier molecule of micronutrients.
Mangiferin protected against gastric injury by ethanol and indomethacin most possibly through the anti-secretory and antioxidant mechanisms.
Mangiferin also together with epigallocatechin gallate has been found to be able to have protective effect on lipid peroxidation in red blood cells, possibly due to its antioxidant activity.
It has also shown anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects. This xanthone was to possess anti-gro0wth effects in ascitic fibro sarcoma by both in vitro and in vivo studies.
Phytochemical mangiferin of mango fruit
Mangiferin was found to have cardio-protective activity. Recent studies showed that mangiferin and mango extracts rich in mangiferin increased endothelial cell migration.
In one study dietary administration of mangiferin inhibited benzene (a) pyrene- induce lung carcinogenesis in Swiss albino mice.
The result suggested that mangiferin present in mango extracts may have health promoting effects in diseases related to the impaired formation of new blood vessels.
The formation of new blood vessels is an important therapeutic target for diseases such as limb ischemia, coronary infarction or stroke.
It also reported that mangiferin inhibits tumor growth in early and late stages of cancer.
The easiest source of mangiferin is the mango plant – Mangifera indica, especially the leaves of the plant. Stem bark, heartwood and roots of Mangifera indica also yield mangiferin. It is synthesized in leaves and remains stored at bark. During flushing, mangiferin is mobilized into the growing region and is utilized in forming new shoots and leaves.
Mangiferin being phenolic in nature also acts as a defensive chemical compound of the plant. Besides it serves as the carrier molecule of micronutrients.
Mangiferin protected against gastric injury by ethanol and indomethacin most possibly through the anti-secretory and antioxidant mechanisms.
Mangiferin also together with epigallocatechin gallate has been found to be able to have protective effect on lipid peroxidation in red blood cells, possibly due to its antioxidant activity.
It has also shown anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects. This xanthone was to possess anti-gro0wth effects in ascitic fibro sarcoma by both in vitro and in vivo studies.
Phytochemical mangiferin of mango fruit
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Popular articles
-
Nutritional Role of Protein Protein accounts for about 10–15 percent of energy in human diets and is indispensable for life. It forms the st...
-
Antioxidant activity (AA) measures a substance’s ability to counteract free radicals—unstable molecules that cause oxidative damage to cells...
-
Flavonoids are a diverse group of plant-based secondary metabolites, primarily consisting of a benzopyrone structure with various phenolic o...
-
Food plays a vital role in regulating the body's hormones and brain chemicals. Once digested into glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids,...
-
The element that was previously considered to be toxic turned out to be present in the human body in amounts of 10–15 mg, and almost every c...