Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan found in the fluids in the eyes and joints. It acts as a cushion and lubricant in the joints and other tissues. In 1934, Karl Meyer and his assistant, John Palmer, described a procedure for isolating a novel glycosaminoglycan (GAG) from the vitreous of bovine eyes. They showed that this substance contained an uronic acid and an amino sugar but without sulfoesters.
The term hyaluronan is attributed Endre Balazs, who coined it to encompass the different form the molecule can take for example the acid form, Hyaluronic acid and the salts such as sodium hyaluronate, which form at physiological pH.
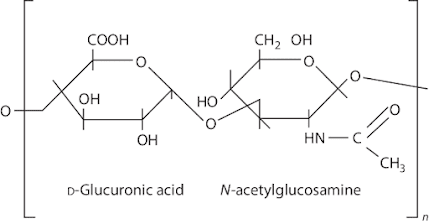
Its name is derived from hyaloids (vitreous) and uronic acid. Hyaluronic acid is a polyanionic natural polymer occurring as linear polysaccharide composed of glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine repeats via a β-1,4 linkage. The size of hyaluronic acid appears to be of critical importance for its various functions. A of high molecular size, usually in excess of 1,000 kDa, is present in intact tissues and is antiangiogenic and immunosuppressive, whereas smaller polymers of hyaluronic acid are distress signals and potent inducers of inflammation and angiogenesis.
Hyaluronic acid is a typical mucopolysaccharide. It is a naturally occurring substance found in the spaces between the cells of body tissues in all animals. Hyaluronic also known as hyaluronan.
Hyaluronic acid is a humectant — a substance that retains moisture — and it is capable of binding over one thousand times its weight in water. The largest amounts of it are found in skin, connective tissue and eyes. Its main function is to retain water to keep tissues well lubricated and moist. It is also found in the capsular component of certain bacterial such as Streptococcus sp. and Staphylococcus sp.
Hyaluronic acid is synthesized in many cell types, but primarily in the plasma membrane of fibroblasts. Physiologically, hyaluronic acid has a role in several process including angiogenesis, extra cellular matrix, homeostasis, wound healing and the mediation of long-term inflammation. The synthesis of hyaluronic acid increases during tissue injury and wound healing and hyaluronic acid regulates several aspects of tissue repair, including activation of inflammatory cells to enhance immune response and the response to injury of fibroblasts and epithelial cells.
Hyaluronic acid
Nutrition is a scientific discipline that encompasses a structured body of knowledge. It includes various fields such as clinical nutrition, community nutrition, public health, food policy, and food science. At its core, nutrition is the study of how the body utilizes food. It is essential to life. Understanding nutrition enables us to make better dietary choices by determining the necessary nutrient intake, identifying optimal food sources, and recognizing beneficial or harmful food components.
Popular articles
-
Fruits Beverage Fruit always played an important role in human nutrition. However, before the 20th century, drinking squeezed fruit juice wa...
-
Digestive enzymes are often used to support healthy digestion and increase nutrient absorption. Naturally occurring digestive enzymes are pr...
-
Saccharin is an artificial sweetener that provides sweetness without food energy or calories. It is one of the earliest sugar substitutes, h...
-
Dark green leafy vegetables contain two pigments, lutein and zeaxanthin, that accumulate in the eye. They appear to be able to snuff out f...
-
The papaya is an amazingly rich source of the proteolytic enzymes, papain. Papain is used tenderized meat, clarify beer, treat digestive dis...