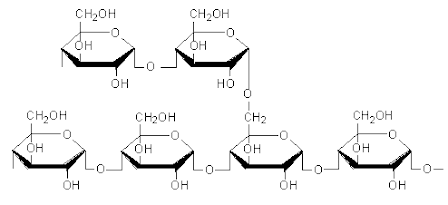
Amylopectin is one of the biggest molecules in nature being the principal component in the majority of starches. Starches with varying amylose and amylopectin content are of particular interest due to their ability to influence and modify the texture, quality and stability of starch-based food products.
Starch normally contains about 20–30% amylose and 70–80% amylopectin. Amylopectin consists of numerous chains that are much shorter than the major chains found in amyloses.The branched amylopectin molecule contains regions with low and high levels of branches. The branches in amylopectin constitute about 5% of the molecule, which results in a very complex molecular structure. Short chains of amylopectin form double-helices, which crystalize and contribute to the semi-crystalline nature of the starch granules.
In highly branched regions, side-chains of amylopectin are grouped, forming crystalline zones (clusters). Side chains of the amylopectin molecule can be divided in A, B, and C chains. The A chains are the shortest.
C chains constitute the backbones of the amylopectin molecules, to which B-chains are linked that at the same time carry one or more branches. The B chains are classified into B1, B2, B3 and B4 depending on their length and the number of clusters that they span.
Amylopectin
Nutrition is a scientific discipline that encompasses a structured body of knowledge. It includes various fields such as clinical nutrition, community nutrition, public health, food policy, and food science. At its core, nutrition is the study of how the body utilizes food. It is essential to life. Understanding nutrition enables us to make better dietary choices by determining the necessary nutrient intake, identifying optimal food sources, and recognizing beneficial or harmful food components.